 Linear Bearings / Slides
Linear Bearings / Slides
ISC Companies and affiliate Adams-ISC are distributors of mechanical power transmission parts including linear bearings. For more information about the brands we offer and/or pricing, please contact us by phone 763-559-0033, by email [email protected], or by filling out our online contact form.
Linear motion bearings, also called linear slides, provide low-friction motion in one direction. Linear bearings usually have a stationary support called a rail, way, or guide. A block, also called a shoe or carriage, slides forward or backward in a straight line along the rail. Seals are typically on the block to help keep contaminants out and wipe the rail. There are three basic block designs: box way, dove tail, and round rail. Linear bearings can incorporate both rolling elements and plain sliding surface bearings.
Rolling Element Bearing Designs
- Ball Bearings: Recirculating balls travel through the carriage, entering and leaving the load carrying zone. These are popular because of their low-friction, long life, and accuracy.
- Roller Bearings: Roller bearings are more rigid, carry more load, and are tolerant of shock loads, but they do not tolerate as much misalignment as ball bearings.
Non-Recirculating and Recirculating Configurations
Rolling element designs incorporate precision steel balls in two configurations: non-recirculating (small range, low friction) and recirculating (unlimited range).
- Non-recirculating assemblies use a carrier containing a straight line of steel balls, separated by a cage. The steel balls rub up against one another.
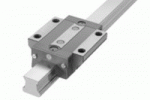 Recirculating designs have a channel in the slider that allows the balls to roll on a path. The two formats are the circular arch (two-point contact) and Gothic arch (four-point contact).
Recirculating designs have a channel in the slider that allows the balls to roll on a path. The two formats are the circular arch (two-point contact) and Gothic arch (four-point contact).
Plain Bearing Designs
Plain bearings (also called bushings and sleeve or journal bearings) incorporate a stationary rail, covered by a bearing slider that is low-friction and self-lubricating. A thin layer of lubricant is maintained between sliding surfaces.
Plain bearings are higher friction and have poor positioning accuracy, but they have a high load capacity, reduced weight, lower cost, and are low maintenance. Many plain linear bearings are being replaced by rolling element linear bearings in high-precision and high-speed applications .
There are three general classes of plain bearings:
- Class I: An outside source of lubrication is required.
- Class II: Lubrication is impregnated in the walls. May need additional lubricant.
- Class III: Self-lubricating bearings that do not require additional lubrication.
Linear Guide Profile Shapes
Round Shaft (Round Rail, Linear Bearings, Linear Ball Bushings)
Has three or more circuits of balls in rolling contact with the shaft and bearing raceways. Most linear ball bushings are solid cylinders, though some are split axially to allow for preloading. Split linear ball bushings are preloaded on a shaft when the bearing is forced into an interference-fit housing.
Ball Splines
Ball splines are a subcategory of round shaft products. Typical round shaft products can move back and forth and rotate around the shaft. Ball splines have grooves down the length of the shaft preventing rotation and limiting movement to one direction. There are a few key benefits of ball splines:
- Transmit torque
- Will not slip in the rotational direction
- Have an increased contact angle and can carry more load than a comparably sized traditional bearing
Profile Rail (Square Rail, Linear Guides)
Consist of a carriage (slider, truck, runner, block, etc.) containing rolling elements that continuously ride on supported rails. Rolling elements roll along raceways formed by grooves along the rail and carriages. They are turned around by return guides in the end caps and redirected back to the other end.
Profile rail linear guides are referred to by size, which is the width across the base of the rail in millimeters. They offer twice the load capacity and rigidity compared to the same sized profile rail ball guides, but the rotational degree of freedom in the round rail ball bearings is lost, meaning allowable installation tolerances are tighter.
Cam Roller (Guide Wheel)
Cam rollers can be constructed from either ball or roller bearings. They offer design freedom and can be installed at a low cost. Guide wheels have profiled circumferences that roll on a track with complementary profile-running surfaces. Running-surface profile types include flat or crowned roller wheels with flat track, round profile wheels with round track, and vee profile wheels with vee track.
Guide wheel design permits high load capacities with smooth rolling action. They are ideal for dirty environments because the rolling elements travel through sealed internal raceways. Guide wheels can also be used in rotary and curvilinear applications. Carriage plates can be custom made with wheel mounting positions that match the curve of a specific track.
- Flat / Crowned Roller Wheels: have cylindrical running surfaces. Crowned roller guide wheels have convex curvatures on their running surfaces, which reduces stress.
- Round Profile Wheels: have concave, semicircular running surfaces and are used on rods or rails.
- Vee Profile Wheels: have one or two vee profiles on their circumferences and roll on complementary angle vee tracks. The most common angles are 70 and 90 degrees.
Crossed Roller
Crossed roller slides or bearings are the most accurate form of mechanical linear motion. The cylinder rollers crisscross each other at a 90 degree angle. They are usually used in pairs.
Crossed rollers offer twice the load capacity, five times the life expectancy, less noise, and increased vibration resistance than ball units. Disadvantages include limited travel and they are typically more expensive and harder to assemble.
Telescopic Slides
Also known as drawer slides, telescopic slides fall into two categories, commercial and industrial. Most do not fully extend and only expand in one direction.
Fluid Bearings (Air Bearings, Hydrostatic Bearings)
Rely on a thin layer of liquid or gas to lift the system off the mating surface, allowing for nearly friction-less motion. There are two categories: hydrostatic and fluid dynamic bearings. Hydrostatic bearings are externally pressurized with a pump and the fluid is air, oil, or water. Fluid bearings are expensive and used as a last resort.
- Advantages: less noise, zero wear, infinite life, no lubrication, and very high acceleration and velocity.
- Disadvantages: high power consumption from constant pump operation, low tolerance for extreme temperatures, fluid leakage, and support systems (pumps/filters) require regular maintenance.
Top Brands We Offer
 Content on this page was created using excerpts from the Power Transmission Handbook (5th Edition), which is written and sold by the Power Transmission Distributor’s Association (PTDA).
Content on this page was created using excerpts from the Power Transmission Handbook (5th Edition), which is written and sold by the Power Transmission Distributor’s Association (PTDA).



















You must be logged in to post a comment.